Knee pain at night affects millions of people, with research showing that up to 75% of individuals with severe osteoarthritis experience nocturnal knee pain. This nighttime discomfort doesn't just interrupt sleep; it creates a cycle where poor rest amplifies pain perception, leading to decreased quality of life and impaired daily function.
If you're among the 25% of adults (Am Fam Physician) who experience knee pain, you understand how challenging it can be when that discomfort intensifies at bedtime. The good news is that effective relief strategies exist, from immediate comfort measures to advanced therapeutic technologies like TENS therapy that work with your body's natural pain-relief mechanisms.
Understanding knee pain: Common causes and triggers
Before exploring nighttime relief strategies, it's important to understand what might be causing your knee pain.
Common causes include:
-
Knee osteoarthritis (OA): The most prevalent form of arthritis, affecting joint cartilage and causing pain that often worsens with activity and settles at night. Research shows nocturnal pain prevalence increases dramatically with OA severity—from just 3.6% in those without OA to 75% in severe cases (Arthritis Care Res).
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: An autoimmune condition causing joint inflammation that can flare during periods of rest.
-
Meniscus tears: Cartilage damage that can cause pain during movement and when lying in certain positions.
-
Bursitis: Inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the knee joint, often resulting from overuse or direct trauma.
-
Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons around the knee, commonly affecting the patellar tendon.
-
Previous knee injuries: Old sprains, strains, or fractures that may cause ongoing discomfort, particularly during weather changes or periods of inactivity.
-
Overuse injuries: Pain resulting from repetitive activities or sudden increases in physical activity.
Why knee pain intensifies at night
Understanding why knee pain worsens at night can help you address the root causes more effectively. Several physiological and psychological factors contribute to this phenomenon:
Physical factors
-
Inflammatory response: When you're active during the day, movement helps circulate synovial fluid that lubricates your joints. Once you become inactive, this natural lubrication decreases, leading to joint stiffness and increased inflammation.
-
Accumulated stress: Daily activities place cumulative stress on knee joints. Walking, climbing stairs, and even prolonged sitting can contribute to pain that becomes more noticeable hours later when you're trying to rest.
-
Circulatory changes: Lying down alters blood flow patterns, which can increase swelling in affected joints and surrounding tissues.
Psychological factors
-
Reduced distraction: During busy days, your attention is divided among many tasks. At night, with fewer distractions, you naturally become more aware of physical discomfort, which can make knee pain worse.
-
Sleep position stress: Certain sleeping positions can place additional pressure on already sensitive knee joints, exacerbating pain.
Seven immediate relief strategies for tonight
When knee pain is keeping you awake, these evidence-based strategies can provide relatively quick relief and reduce knee pain:
1. Targeted stretching and movement
Gentle stretching before bed helps improve circulation and reduce muscle tension around the knee joint. Focus on these key areas:
-
Hamstring stretch: Stand with one leg extended, heel on the floor and toes up. Gently bend forward from your hips while slightly bending your standing knee. Hold for 20-30 seconds per leg. This releases tension in muscles that support knee function.
-
Quadriceps stretch: Lying on your side, bend your top knee and gently pull your foot toward your buttocks. This stretch relieves pressure on the kneecap and surrounding structures.
-
Calf stretch: Tight calf muscles can contribute to knee pain. Stand arm's length from a wall, place your hands against it, and step one foot back, keeping the heel down and leg straight.
2. Optimize your sleep environment
Creating the right conditions for sleep can significantly impact pain perception:
-
Temperature control: Keep your bedroom between 65-68°F (18-20°C). Cooler temperatures can help reduce inflammation.
-
Support your position: Use pillows strategically to reduce pressure on painful joints. Side sleepers should place a pillow between their knees, while back sleepers benefit from a pillow under the knees.
-
Minimize disruptions: Use blackout curtains, white noise machines, or earplugs to create an environment conducive to deeper sleep.
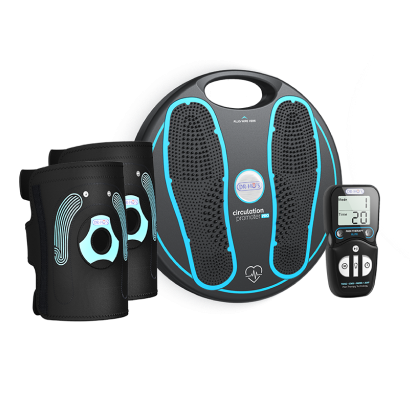
3. Advanced TENS Therapy
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) represents one of the most effective non-pharmaceutical approaches to managing knee pain.
DR-HO'S proprietary AMP Technology combines TENS with EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) and NMES (Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation) in an innovative 4-in-1 system that works with your body's natural pain-relief mechanisms
How TENS technology works
TENS therapy delivers gentle electrical impulses that interact with nerve pathways, effectively interrupting pain signals before they reach the brain. This process, based on the gate control theory of pain, provides temporary relief while encouraging the release of endorphins—your body's natural pain-relieving hormones.
While TENS targets nerve pathways, EMS stimulates healthy muscle contractions that increase local blood circulation. This enhanced circulation delivers oxygen and nutrients to affected tissues while helping remove metabolic waste products that can contribute to pain and inflammation.
DR-HO'S AMP Technology combines these therapies in a way that maximizes therapeutic benefit. The synchronized stimulation encourages both nerve and muscle interaction, providing comprehensive relief that addresses multiple pain mechanisms simultaneously.
How to use it:
For knee electrode placement, we recommend ‘sandwiching’ the knee with the large pads:
-
Place a large pad on either side of your knee
-
Note: The pads should not be directly over the actual kneecap
To use TENS therapy for nighttime knee pain, simply place the therapy pads around your knee area, select your preferred intensity level, and let the device work for 20-30 minutes before sleep.
The gentle, massage-like sensation is both therapeutic and relaxing, making it an ideal addition to your bedtime routine.
4. Thermal therapy
Strategic use of heat and cold can provide significant pain relief:
-
Heat application: Apply a heating pad or warm compress for 15-20 minutes before bed. Heat increases blood flow, relaxes muscles, and can help reduce stiffness.
-
Cold therapy: Follow heat treatment with 10-15 minutes of cold therapy using an ice pack wrapped in a thin towel. This helps reduce inflammation and can numb pain signals.
-
Contrast therapy: Alternating between heat and cold can be particularly effective for reducing swelling and managing pain.
5. Warm bath therapy
Research demonstrates that bathing in water heated to 104-109°F (40-43°C) approximately 90 minutes before bedtime can help people fall asleep 10 minutes faster on average. Warm baths provide multiple benefits for knee pain:
-
Reduced gravitational pressure on joints
-
Improved circulation
-
Muscle relaxation
-
Overall stress reduction
6. Compression and support
Knee braces or compression sleeves can provide several benefits for nighttime pain relief:
-
Improved proprioception (joint position awareness)
-
Reduced swelling through gentle compression
-
Enhanced joint stability
-
Psychological comfort
Choose a brace that provides adequate support without being too tight, as excessive compression can interfere with circulation.
7. Mindfulness and distraction techniques
Managing the psychological component of pain is crucial for better sleep:
-
Guided meditation: Apps offering sleep-focused meditations can help redirect attention away from pain while promoting relaxation.
-
Progressive muscle relaxation: Systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups can reduce overall tension and pain perception.
-
Breathing exercises: Deep, controlled breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing pain sensitivity.
-
Audio distraction: Light podcasts, audiobooks, or nature sounds can provide gentle distraction without being stimulating enough to interfere with sleep.
Long-term strategies to ease knee pain
While immediate relief strategies are important, addressing knee pain comprehensively requires a long-term approach:
Activity modification
-
Pacing: Distribute demanding activities throughout the day rather than concentrating them in short periods.
-
Low-impact exercise: Swimming, cycling, and elliptical training can maintain joint health without excessive stress.
-
Strengthening: Focus on the quadriceps, hamstrings, and hip muscles that support knee function.
Weight management
Even modest weight loss can significantly reduce knee joint stress. Each pound of body weight translates to approximately 4 pounds of pressure on the knees during walking.
Footwear and support
Proper footwear with adequate arch support can prevent biomechanical issues that contribute to knee pain. Custom orthotics may be beneficial for individuals with significant foot structure abnormalities.
See your healthcare provider or physical therapist
Persistent nighttime knee pain warrants professional evaluation. Healthcare providers can:
-
Identify underlying conditions requiring specific treatment
-
Recommend appropriate imaging studies
-
Suggest targeted physical therapy interventions
-
Discuss medication options (including pain relievers) when conservative measures are insufficient
The impact of quality sleep on pain management
Research consistently demonstrates the bidirectional relationship between sleep and pain. Poor sleep increases pain sensitivity, while effective pain management improves sleep quality. Studies (Arthritis Care Res) show that individuals with both osteoarthritis and sleep disturbances have significantly lower quality of life scores compared to those with OA alone.
Breaking this cycle requires addressing both components simultaneously. The strategies outlined above work synergistically—thermal therapy and TENS can provide immediate pain relief, while improved sleep hygiene and stress management techniques support long-term pain management success.
Conclusion: Don't let knee pain rob you of quality sleep
Nighttime knee pain affects a substantial portion of adults, with prevalence increasing dramatically in those with osteoarthritis. However, multiple evidence-based strategies can provide effective relief:
-
Immediate relief comes from proper positioning, thermal therapy, and advanced technologies like TENS
-
Comprehensive management requires addressing both physical and psychological components of pain
-
Long-term success depends on lifestyle modifications and professional guidance when needed
Remember that effective pain management is often multifaceted. What works best to relieve pain for you may be a combination of several approaches. Start with the immediate relief strategies that seem most applicable to your situation, and don't hesitate to seek professional guidance if pain persists or worsens.
Quality sleep is not a luxury—it's essential for health, healing, and overall well-being. The DR-HO’S JustRight Pillow with its Adjust-to-Fit Technology is designed to give you a good night’s rest. With the right combination of strategies and tools, you can break the cycle of pain and sleeplessness, returning to the restorative rest your body needs.
Disclaimer: DR-HO'S content is intended for informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please consult a certified medical professional for diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Additional Sources:
1. Health Essentials Why Do I Have Knee Pain at Night?
2. Healthline How to Ease Knee Pain and Sleep Tight Through the Night
3. Medical News Today How to get rid of knee pain when sleeping
4. WebMD Knee Pain Do’s and Don'ts
5. U.S. News Is Your Knee Pain Worse At Night? 6 Ways To Improve Pain
6. Healthline Having Trouble Sleeping? Try a Hot Bath Before Bed