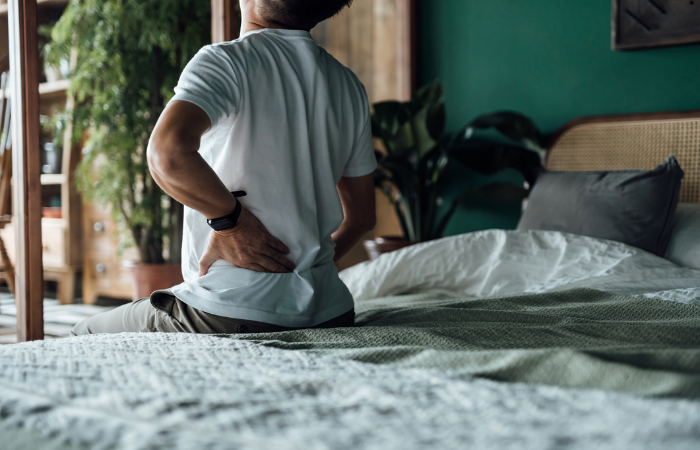
Suffering from Stiff and Tight Back Muscles? You’re Not Alone.
Are you experiencing sharp back pain and having difficulty moving? It could be a result of stiff and tight muscles in the back. In fact, muscle stiffness is one of the most common causes of muscle pain.
Keep reading to learn just how muscle stiffness actually translates to back pain, and more importantly some tips on how to help ease that back pain when it flares up.

How Do Stiff and Tight Muscles Result in Back Pain?
To understand how tight muscles can lead to pain, we first need to understand some basic human anatomy on nerves and muscles.
1) Nerves: cable-like structures located all throughout the body.
- Their main purpose is to relay information from one part of the body to another.
- Motor nerves carry the messages from the brain through the spinal cord to other parts of the body such as the muscles.
2) Muscles: soft tissues made up of stretchy fibres, for example the lats in the back.
- Muscles allow our bodies to move.
- The muscular system is controlled via the nervous system.
How Nerves & Muscles Work Together:
The end of each motor neuron sits very close to a muscle fibre, and is thus called a neuromuscular junction. At this point:
- The motor neuron releases a message
- It is picked up by the muscle fibre
- This tells the muscle fibre to contract
- In turn, the muscle moves
When it comes to pain:
- The nerve sends the brain the signal of pain when organs or tissues are irritated or close to being damaged
- In reaction, the brain sends back signals to muscles to take appropriate action
- For example, if your hand gets too close to a stove, the nerves send a pain signal to the brain and you pull back before you burn yourself
What Happens to Nerves when Muscles are Tight?
When muscles are stiff and tight, they can constrict or pinch the nerves at the neuromuscular junction. The nerve will send this signal back to the brain, causing the feeling of irritation, pain, pins and needles, and numbness.
Now that we know what happens to our bodies when muscles are stiff, let’s take a look at how muscles can become stiff in the first place.
What Causes Stiff & Tight Back Muscles?
There are a few different potential causes of stiff and tight back muscles. These include:
1. Muscle Overuse
It’s very common to experience back muscle stiffness after periods of strenuous exercise. This can be from hard physical work, running long distances, or lifting weights (especially movements that involve pulling or lifting).
2. Periods of Inactivity
It’s also possible to feel muscle stiffness after periods of inactivity, such as when getting out of bed in the morning or getting out of a chair after sitting for a long time.
3. Acute Injury
An accident or sports injury that involves a blow to the back, especially through a sprain can lead to tightness in the back muscles. These injuries cause inflammation and swelling that often lead to or come with muscle tightness.
4. Arthritis
If you’ve been diagnosed with spinal arthritis, you will likely experience stiffness and pain in the muscles of the back from inflammation.
How to Help Reduce Stiff & Tight Back Muscles and Minimize Pain
1. Stretch
The natural reaction to pain in the back is often to rest. And while this can help in the moment of pain, stretching can be very beneficial as it helps muscles relax and increases blood flow to the area. Here are a few back-friendly stretches:
Cat-Cow:
Start on your hands and knees with your back straight and your head and neck in line. On an inhale, drop your belly toward the ground and look up toward the ceiling (cow pose). On an exhale, tuck in your stomach, arch your back and lower your head to your chest (cat pose). Do it gently, and stop if you feel any pain.
Back-pocket Stretch:
Stand up and place both hands behind you as if you’re putting them in the rear pockets of your jeans, hold your left wrist with your right (or vice versa); look up and extend (arch) your back.
Press Up (or Cobra):
Start by lying on your stomach and place both hands parallel on the floor as if you were starting to do a push-up. Then gently engage your lower back, buttocks, and thighs as you lift your head and chest. Stay strong in your lower back and abdominals while breathing deeply. Hold this pose for 30 seconds to 1 minute and repeat 5-8 times.

2. Gentle Exercise
Unless otherwise directed by your preferred healthcare provider, don’t stop moving due to your pain! This is especially important for those whose upper back pain comes from muscle stiffness.
Light activities include:
- Walking slowly
- Doing light household chores such as putting away groceries or folding laundry
Just ensure that:
- These activities don’t involve excessive bending or twisting
- If you’re doing anything intense, you’re stretching beforehand
3. Heat Therapy
Heat application can also be quite helpful for relieving pain from back stiffness. Apply heat to your pain-affected areas with gels, creams or heating pads, or visit a sauna, hot tub, or take a warm bath at home. Whichever application you choose, heat therapy can improve blood circulation to promote healing of damaged tissues and help stretch tissues, reducing uncomfortable stiffness.
4. Physical Therapy
Depending on the severity of your muscle tightness, a simple routine of gentle stretching may be enough to improve your symptoms. However more serious muscle tightness may require a program of physical therapy focused on motions that stretch and lengthen muscle tissue.
5. TENS Devices
If you're unable to make it to a physical therapist office, why not try the tools that are often used in those clinics? TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation) machines are one such pain therapy tool.
TENS machines are small, compact devices that produce gentle electrical currents conducted through small pads placed on the body. This stimulation targets the nerves, temporarily reducing pain signals. In addition, TENS therapy is thought to trigger the release of endorphins, natural hormones produced by our bodies to help temporarily relieve pain.
DR-HO’S carries a line of TENS products specifically designed for the back:
- Triple Action Back Belt – for the lower back
- Neck Pain Pro – for the upper back and shoulders
- Pain Therapy System – for full body use, wherever you experience pain
These DR-HO’S TENS devices also use EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) Therapy, which targets and penetrates muscles, causing them to contract and relax. As these healthy muscles start to contract and move, the EMS stimulation can help temporarily increase local blood circulation, bringing nutrient rich, oxygenated blood to those muscles.
Start the Path to Back Pain Management
Muscle stiffness is one of the most common causes of muscle pain, whether it's from excessive exercise or an acute injury. But there are steps you can take to minimise your back pain! We hope you test out a few of these techniques and can find some relief to stiff back pain.
At DR-HO’S we are on a mission to develop and promote drug-free, effective pain therapy devices to help people live a life with less pain. Pain should not rob you of your quality of life and prevent you from participating in your favourite activities – and it’s a devastating reality, that for many it does. Learn more about our philosophy and the possibility for hope, here.
Back pain from muscle stiffness is temporary and should resolve itself in a short amount of time. However if soreness persists beyond two weeks, please contact your healthcare professional.